Vision matters! Did you know diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness among working-age adults? Don’t turn a blind eye, discover the facts now
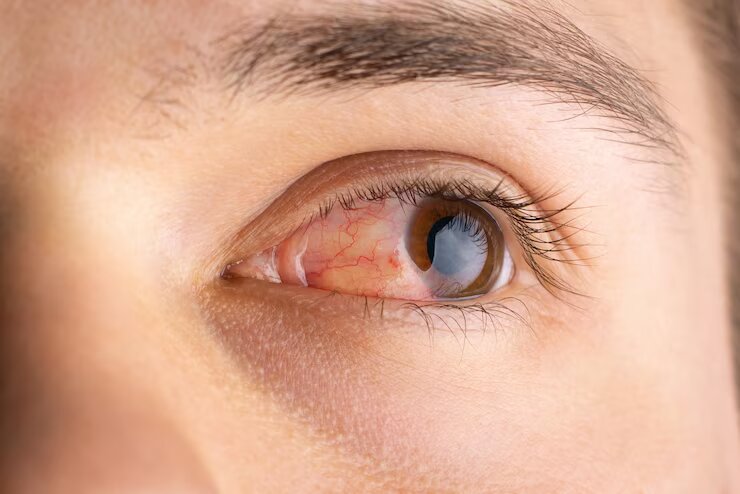
Diabetic retinopathy, a condition affecting the eyes, is a serious complication of diabetes. Understanding its causes, symptoms, stages, treatment, and prevention is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this eye condition and explore ways to manage and prevent its impact.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive eye disease that stems from long-term diabetes. The retina, a crucial part of the eye responsible for capturing images, undergoes changes due to high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes.
Prevalence:
- Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes, affecting a significant number of individuals worldwide.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness among working-age adults.
Risk Factors:
- Duration of diabetes: The longer an individual has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Poorly controlled blood sugar levels: Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is crucial in preventing and managing diabetic retinopathy.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can contribute to the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Causes of Diabetic Retinopathy
The primary cause of diabetic retinopathy is the sustained elevation of blood sugar levels. Over time, this damages the blood vessels supplying the retina, leading to a range of complications.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
As the condition progresses, individuals may experience vision problems, including blurred or fluctuating vision, floaters, and dark spots. Gradual vision loss is a common symptom and often indicates advanced stages of the disease.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is categorized into two main stages: non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Understanding these stages is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR):
NPDR is the early stage of diabetic retinopathy. In this stage, the blood vessels in the retina are damaged due to prolonged exposure to high levels of blood sugar. The key characteristics of NPDR include:
- Microaneurysms: Small bulges in the blood vessels of the retina, which can leak fluid into the surrounding tissues.
- Retinal Hemorrhages: Occasional bleeding from the damaged blood vessels, leading to the presence of small dot-like hemorrhages.
- Hard Exudates: Yellow deposits formed by leaked fats and proteins, which accumulate in the retina.
- Macular Edema: Swelling in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. This can result in blurred or distorted vision.
While NPDR is the early stage and may not cause significant vision problems initially, it serves as a warning sign. Timely detection and management at this stage are crucial to prevent progression to more severe forms of diabetic retinopathy.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR):
PDR is the advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy, characterized by the proliferation of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. Key features of PDR include:
- Neovascularization: Abnormal blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina and into the vitreous gel, the jelly-like substance that fills the eye.
- Vitreous Hemorrhage: Bleeding from the abnormal blood vessels into the vitreous, leading to floaters or sudden vision loss.
- Retinal Detachment: Scar tissue forms as a result of the abnormal blood vessels, pulling the retina away from the back of the eye. This can cause severe vision loss.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure in the eye due to neovascularization can lead to glaucoma, further impacting vision.
PDR is a more critical stage and poses a higher risk of severe vision impairment or blindness. Timely intervention, often through laser surgery or other advanced treatments, is crucial to manage the condition and prevent irreversible damage.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Regular eye examinations and tests are essential for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy in its early stages. Diabetics should prioritize eye health check-ups to detect and manage any developing complications promptly.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options exist, including laser surgery, vitrectomy, and anti-VEGF medications. Each approach targets specific aspects of diabetic retinopathy, aiming to preserve vision and prevent further damage.
Prevention Strategies
Managing diabetes effectively is key to preventing diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to a balanced diet contribute significantly to minimizing the risk of complications.
Living with Diabetic Retinopathy
Coping with diabetic retinopathy involves adopting strategies to manage daily challenges. Support networks and adaptive technologies play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals dealing with this condition.
The Role of Nutrition in Eye Health
A well-balanced diet rich in nutrients such as vitamins A, C, and E, omega-3 fatty acids, and zinc can contribute to maintaining optimal eye health. Incorporating these nutrients into one’s diet can support overall eye function.
Impact of Diabetic Retinopathy on Daily Life
The challenges faced by individuals with diabetic retinopathy are diverse. However, adaptive technologies and support systems can assist in overcoming obstacles, allowing individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
Research and Innovations
Ongoing research in the field of diabetic retinopathy promises advancements and potential breakthroughs. Keeping abreast of these developments is crucial for individuals and healthcare professionals alike.
The Importance of Spreading Awareness
Community education initiatives are pivotal in spreading awareness about diabetic retinopathy. Empowering individuals with knowledge enables proactive management, fostering a sense of control over eye health.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious concern for individuals with diabetes, but understanding its causes, symptoms, stages, treatment, and prevention empowers proactive management. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and advancements in research collectively contribute to mitigating the impact of this condition.
FAQs
- Why is early detection crucial for diabetic retinopathy?
- Early detection allows for timely intervention and management, preventing irreversible vision loss.
- Can diabetic retinopathy be completely cured?
- While diabetic retinopathy may not be completely cured, early and effective management can significantly slow its progression.
- What lifestyle changes can help prevent diabetic retinopathy?
- Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing blood sugar levels are key lifestyle changes to prevent diabetic retinopathy.
- Are there alternative treatments for diabetic retinopathy?
- Depending on the severity, alternative treatments may be explored, but consultation with a healthcare professional is essential.
- How often should individuals with diabetes have eye check-ups?
- Regular eye check-ups, at least annually, are recommended for individuals with diabetes to monitor and manage any emerging eye-related complications.